What are the symptoms of viral meningitis?
Viral meningitis, an inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord caused by a virus, can present with various symptoms. Common symptoms include:
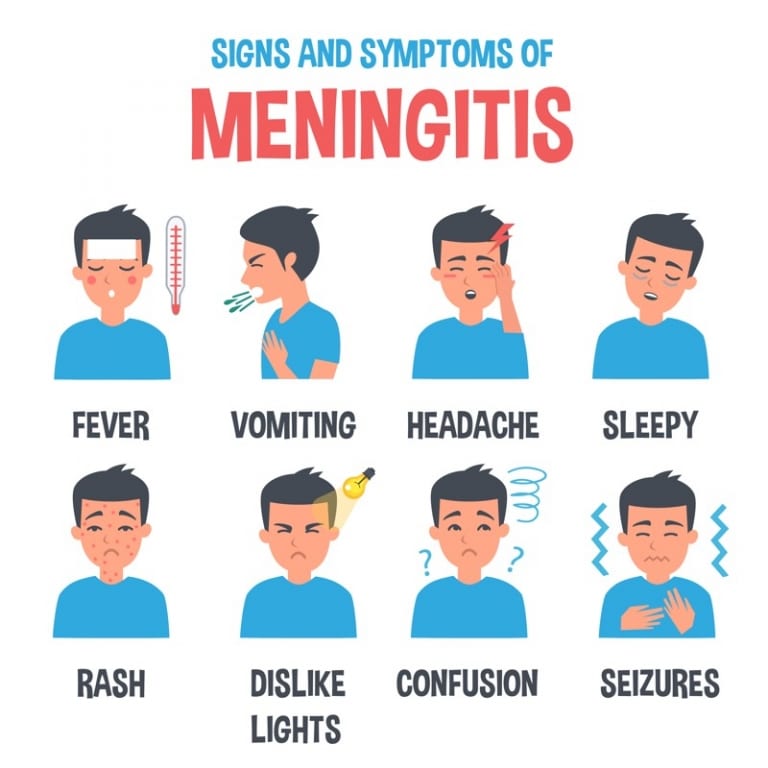
- Headache: Often severe and persistent.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature is typical.
- Stiff Neck: Difficulty moving the neck or pain when trying to bend it.
- Photophobia: Sensitivity to light.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Often accompanying the headache.
- Fatigue: General feelings of tiredness or weakness.
- Rash: In some cases, a rash may develop, depending on the specific virus.
- Confusion or Difficulty Concentrating: Mental status changes, although less severe than in bacterial meningitis.
- Sleepiness or Difficulty Waking: A feeling of drowsiness or trouble waking up.
- Seizures: In more severe cases or in young children.
In infants and young children, symptoms might include irritability, poor feeding, and a bulging fontanel (soft spot on the head).
What are the causes of viral meningitis?
Viral meningitis is caused by various viruses. Common causes include:
- Enteroviruses: These are the most frequent cause and include coxsackieviruses and echoviruses.
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): HSV type 1 and sometimes type 2 can cause viral meningitis.
- Mumps Virus: Can cause meningitis, particularly if not vaccinated.
- Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV): The virus responsible for chickenpox and shingles can also cause meningitis.
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): Can cause meningitis in the context of acute primary infection or as part of HIV-associated complications.
- West Nile Virus: Transmitted by mosquitoes, this virus can cause meningitis.
- Measles Virus: Although less common due to vaccination, measles can lead to viral meningitis.
- Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus: Transmitted by rodents, this virus can cause meningitis.
- Mumps Virus: Historically, a common cause before the widespread use of the mumps vaccine.
Other, less common viruses may also cause viral meningitis, and in some cases, the exact virus causing the infection may not be identified.
What is the treatment for viral meningitis?
The treatment for viral meningitis primarily focuses on supportive care, as there is no specific antiviral treatment for most viral causes. Here’s how it is generally managed:
- Rest: Adequate rest is crucial for recovery.
- Hydration: Maintaining fluid balance is important to prevent dehydration.
- Pain and Fever Relief: Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) can help alleviate pain and reduce fever.
- Hospitalization: In some cases, especially if there are severe symptoms or complications, hospitalization may be required for closer monitoring and supportive care.
For specific viral causes, treatment may vary:
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): Antiviral medications like acyclovir may be used if HSV is suspected.
- Mumps Virus: Supportive care is the main approach, but complications might require additional treatment.
- Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV): Antiviral medications such as acyclovir can be used, particularly if there’s evidence of severe infection.
Antibiotics are not effective against viral infections but may be administered if there is a risk of bacterial infection or to differentiate between bacterial and viral meningitis.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.