What are the symptoms of an underbite?
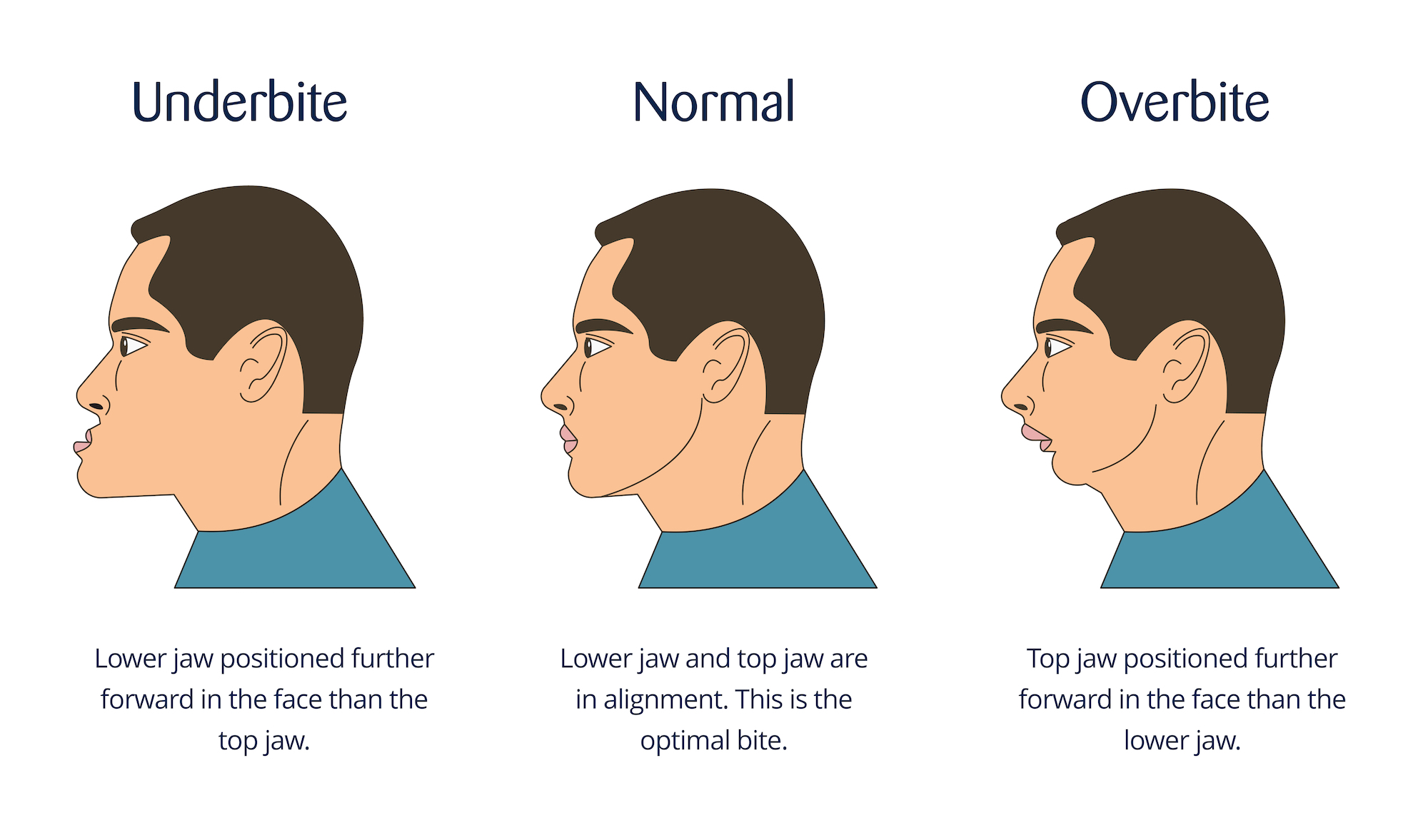
An underbite, or mandibular prognathism, occurs when the lower jaw extends farther out than the upper jaw, causing the lower teeth to overlap the upper teeth. Symptoms of an underbite may include:
- Misaligned Teeth: The lower front teeth may protrude beyond the upper front teeth.
- Difficulty with Chewing and Biting: Eating can be challenging due to misalignment.
- Speech Issues: Problems with pronunciation or clarity of speech may occur.
- Jaw Pain: Discomfort or pain in the jaw, especially when chewing.
- Facial Asymmetry: A noticeable difference in the appearance of the lower and upper jaws.
- Teeth Wear: Uneven wear or stress on the teeth due to misalignment.
- Breathing Problems: Difficulty breathing through the nose if the underbite is severe and affects the airway.
What are the causes of an underbite?
An underbite can arise from various factors, including:
- Genetics: Hereditary factors often play a significant role in the development of an underbite. If one or both parents have an underbite, their children may be more likely to develop it.
- Jaw Development Issues: Abnormalities in the growth and development of the upper and lower jaws can lead to an underbite. This can be due to disproportionate growth rates between the two jaws.
- Prolonged Thumb Sucking: Extended thumb sucking during childhood can affect the alignment of the teeth and jaws, contributing to an underbite.
- Mouth Breathing: Chronic mouth breathing, often due to nasal congestion or other issues, can alter the development of the jaws and teeth.
- Certain Health Conditions: Conditions such as cleft lip and cleft palate, or other congenital anomalies affecting the jaw structure, can lead to an underbite.
- Trauma or Injury: Injuries to the jaw or face can cause misalignment and contribute to the development of an underbite.
- Tumors or Growths: Rarely, tumors or abnormal growths in the jaw can affect its alignment and lead to an underbite.
What is the treatment for an underbite?
The treatment for an underbite typically depends on the severity of the condition and the age of the patient. Common approaches include:
- Orthodontic Treatment: Braces or other orthodontic appliances can help correct mild to moderate underbites by gradually shifting the teeth into proper alignment. This treatment is often effective in children and teenagers whose jaws are still growing.
- Functional Appliances: Devices like the Herbst appliance or the twin block appliance can help reposition the lower jaw to correct the underbite. These are typically used in growing children.
- Dental Procedures: For some cases, dental work such as reshaping or repositioning the teeth may help improve the bite.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases, especially in adults where growth has ceased, orthognathic surgery (jaw surgery) may be necessary. This surgery involves repositioning the upper and/or lower jaw to correct the misalignment and achieve a proper bite.
- Behavioral Modifications: For underbites caused by habits like thumb sucking or mouth breathing, addressing these behaviors can be part of the treatment plan.
- Prosthetics and Restorative Work: In some cases, crowns or dental veneers may be used to improve the appearance and function of the teeth.
Early intervention is often beneficial, so consulting with a dental or orthodontic specialist for personalized treatment recommendations is advisable.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.