What are the symptoms of skin diseases?
Skin diseases can present with a wide range of symptoms, depending on the specific condition. Common symptoms include:
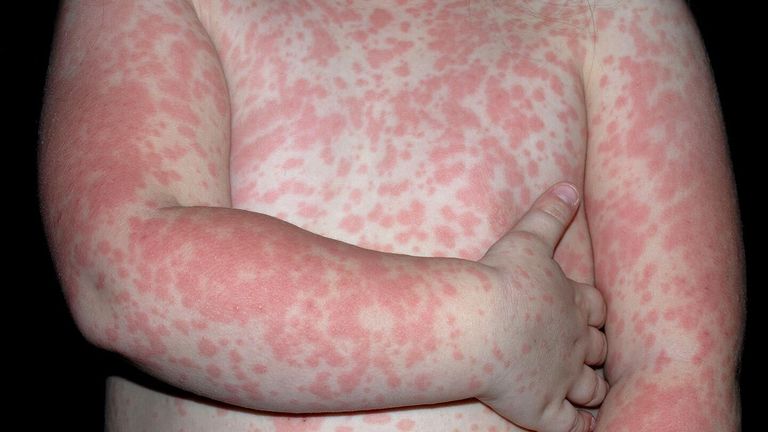
- Rashes: Red, inflamed, or irritated areas of skin.
- Itching: Persistent or severe itching that may accompany other symptoms.
- Dryness: Flaky, scaly, or rough skin.
- Swelling: Puffy or raised areas of skin.
- Blisters: Fluid-filled bumps or sores on the skin.
- Ulcers: Open sores that may be painful or oozing.
- Crusting: Dry, hardened areas that form a crust over a lesion.
- Color Changes: Discoloration, such as redness, paleness, or hyperpigmentation.
- Lesions: Abnormal growths or spots, including moles, warts, or nodules.
- Peeling: Shedding of the outer layer of skin.
- Pain: Discomfort or tenderness in the affected area.
- Burning Sensation: A feeling of heat or discomfort on the skin.
- Hair Loss: Loss of hair in patches or overall thinning.
- Odor: Unpleasant smell, often associated with infections.
- Fever: In some cases, systemic symptoms like fever can accompany skin diseases, especially if there’s an infection.
The specific combination and severity of symptoms depend on the type of skin disease, such as eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis, infections, or skin cancers. For an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist.
What are the causes of skin diseases?
Skin diseases can arise from a variety of causes, including:
- Genetic Factors: Inherited conditions like psoriasis and eczema can be triggered by genetic predisposition.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to allergens, irritants, and pollutants can cause or exacerbate skin conditions.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections, such as ringworm, herpes simplex, and impetigo, can lead to skin diseases.
- Immune System Disorders: Autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the skin.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as those during pregnancy or puberty, can influence skin conditions like acne.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients, such as vitamin A, vitamin C, and vitamin D, can lead to skin problems.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to food, medications, or contact with certain substances can cause skin rashes and irritation.
- Chronic Irritation: Repeated friction or exposure to harsh chemicals can lead to conditions like contact dermatitis.
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays can cause sunburn, premature aging, and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Genetic Mutations: Certain skin cancers and rare skin diseases can be caused by specific genetic mutations.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes and kidney disease can manifest with skin symptoms.
Understanding the underlying cause of a skin disease is essential for effective treatment and management. Consulting a healthcare professional or dermatologist is often necessary to diagnose and address the root cause of the skin issue.
What is the treatment for skin diseases?
The treatment for skin diseases varies depending on the specific condition and its severity. Here are some common approaches:
- Topical Treatments: Creams, ointments, and lotions that contain corticosteroids, anti-fungals, or antibiotics are often used to treat conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and fungal infections.
- Oral Medications: For more severe cases, oral medications such as antibiotics, antifungals, or immunosuppressants may be prescribed. Medications like methotrexate or biologics may be used for conditions like psoriasis or severe acne.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision can help manage conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
- Moisturizers: Regular use of moisturizers can help alleviate dryness and irritation in conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding known triggers, such as allergens or irritants, and adopting a skincare routine suited to the condition can improve symptoms.
- Surgical Interventions: Procedures such as cryotherapy, laser therapy, or surgical removal might be necessary for skin cancers, warts, or certain precancerous lesions.
- Allergy Management: For skin conditions related to allergies, identifying and avoiding allergens is crucial, and antihistamines or corticosteroids may be used.
- Supportive Care: In cases where skin conditions are part of a larger health issue, managing the underlying condition with appropriate treatments can help improve skin symptoms.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Maintaining a balanced diet, preventing dehydration, and protecting skin from excessive sun exposure can aid in overall skin health.
Consulting with a dermatologist or healthcare provider is essential to determine the appropriate treatment plan based on the specific diagnosis and individual needs.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.