What are the symptoms of skin conditions affecting children?
Skin conditions in children can present with a variety of symptoms, which can vary depending on the specific condition. Common symptoms include:
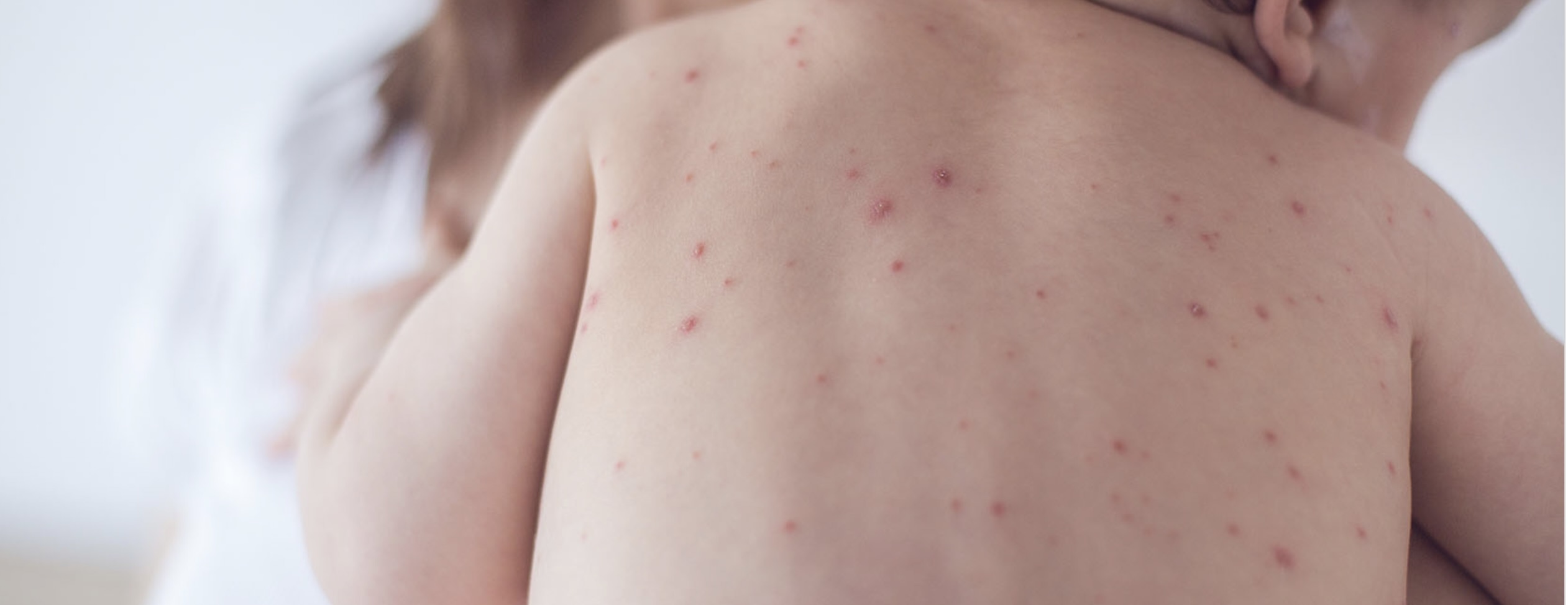
- Rashes: Red, itchy, or inflamed areas of skin. Rashes can appear as patches, spots, or bumps.
- Itching: Persistent itching or discomfort, which can lead to scratching and further skin irritation.
- Dry or Flaky Skin: Areas of skin may become dry, scaly, or peeling.
- Blisters: Fluid-filled sacs that may appear on the skin, often caused by conditions like chickenpox or impetigo.
- Swelling: Areas of skin may become swollen or puffed up.
- Discoloration: Changes in skin color, such as redness, paleness, or dark patches.
- Pain: Some skin conditions can cause pain or tenderness in the affected areas.
- Crusting or Scabbing: Skin may develop crusts or scabs, especially if there has been scratching or an infection.
- Fever: In some cases, skin conditions may be accompanied by fever, especially if an infection is present.
- Sores or Ulcers: Open sores or ulcers can develop in conditions like eczema or infections.
- Warts or Growths: Small, raised areas or bumps, such as warts or moles, may be present.
If a child shows symptoms of a skin condition, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What are the causes of skin conditions affecting children?
Skin conditions in children can arise from various causes, including:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can lead to conditions such as impetigo, chickenpox, or ringworm.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to foods, medications, or environmental factors (like pollen or pet dander) can cause skin issues such as hives or eczema.
- Genetic Factors: Some skin conditions, like eczema or psoriasis, can have a genetic component and may run in families.
- Immune System Disorders: Conditions like autoimmune diseases can affect the skin. For example, lupus can cause skin rashes.
- Environmental Irritants: Exposure to harsh chemicals, soaps, or fabrics can irritate the skin and cause conditions like contact dermatitis.
- Heat and Sweat: Overheating or sweating can lead to heat rash or prickly heat.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate hygiene can contribute to skin infections or infestations such as lice.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients can sometimes lead to skin problems, such as dry or flaky skin.
- Chronic Conditions: Chronic conditions like eczema or psoriasis can cause persistent skin issues.
- Insect Bites: Bites from insects like mosquitoes or fleas can lead to itching, redness, and swelling.
- Skin Trauma: Injuries or friction can cause conditions like abrasions or blisters.
Identifying the underlying cause of a skin condition is crucial for effective treatment, so consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management is important.
What is the treatment for skin conditions affecting children?
The treatment for skin conditions affecting children varies based on the specific condition but often includes:
- Topical Treatments: Creams or ointments containing corticosteroids, antihistamines, or anti-fungal agents can help with inflammation, itching, or infections.
- Oral Medications: For more severe conditions, oral medications such as antibiotics (for bacterial infections), antivirals (for viral infections), or antihistamines (for allergies) may be prescribed.
- Moisturizers: Regular use of emollients and moisturizers can alleviate dryness and manage conditions like eczema.
- Antibiotics or Antifungals: For bacterial or fungal infections, appropriate antibiotics or antifungal medications may be required.
- Antihistamines: These can help with itching and hives caused by allergic reactions.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding allergens, irritants, or other triggers can help manage conditions like eczema or contact dermatitis.
- Good Hygiene Practices: Maintaining proper hygiene can prevent or manage skin infections. This includes regular bathing with mild soaps and keeping the skin clean and dry.
- Specialized Therapies: For chronic conditions like psoriasis or severe eczema, treatments such as phototherapy or systemic medications might be recommended by a dermatologist.
- Insect Bite Management: For insect bites, applying soothing creams and keeping the area clean can reduce discomfort and prevent infection.
- Protective Measures: Using sun protection (like sunscreen) to prevent sunburn or exacerbation of certain skin conditions.
- Dietary Adjustments: In cases where skin issues are related to nutritional deficiencies, ensuring a balanced diet or using supplements as advised by a healthcare professional can be beneficial.
- Behavioral and Environmental Modifications: For conditions exacerbated by environmental factors, such as heat rash, ensuring a cool environment and wearing breathable clothing can be helpful.
Consulting with a healthcare provider or dermatologist is important for a proper diagnosis and to develop an individualized treatment plan tailored to the child’s specific needs.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.