What are the symptoms of a septate hymen?
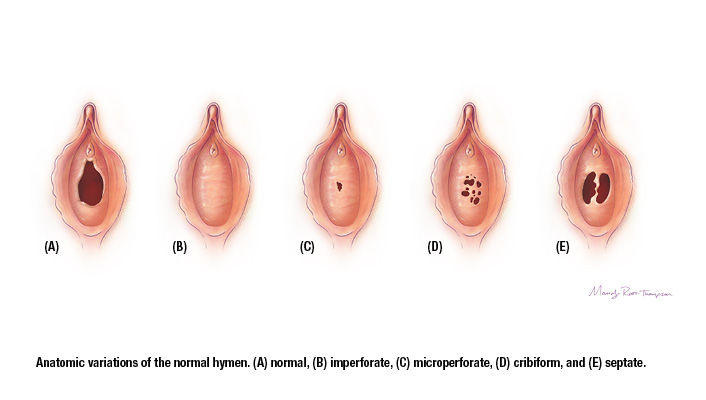
A septate hymen is a congenital condition where the hymen, a thin membrane at the vaginal opening, has an extra band of tissue running down the middle, creating two small vaginal openings instead of one. The symptoms of a septate hymen can vary but may include:
- Difficulty with Tampon Use: Individuals with a septate hymen may find it difficult or uncomfortable to insert tampons due to the extra band of tissue.
- Pain or Discomfort: Some may experience pain or discomfort during tampon use, gynecological exams, or sexual intercourse.
- Menstrual Flow Issues: The presence of the extra tissue band may cause menstrual blood to flow irregularly or make it difficult for menstrual blood to pass through the vaginal opening, leading to issues like spotting or irregular bleeding.
- Vaginal Obstruction: In some cases, the septate hymen can partially block the vaginal opening, which may cause symptoms such as difficulty with vaginal penetration or discomfort during physical activities.
- No Symptoms: In some cases, a septate hymen may not cause any noticeable symptoms, and the condition may only be discovered during a routine gynecological exam or when attempting to use tampons for the first time.
A septate hymen is usually not harmful, but if it causes significant discomfort or other issues, minor surgery (hymenectomy) can be performed to remove the extra band of tissue.
What are the causes of a septate hymen?
A septate hymen is a congenital condition, meaning it is present at birth. The exact cause is related to the normal development of the hymen during fetal growth. During embryonic development, the hymen forms from the urogenital sinus, and as the fetus develops, the hymen typically remains as a thin membrane at the vaginal opening.
In the case of a septate hymen, this membrane develops with an extra band of tissue running down the middle, creating two small vaginal openings instead of one. The development of a septate hymen is not due to any external factors or actions taken during pregnancy; it is simply a variation that occurs naturally as the fetus develops.
Since a septate hymen is a congenital anomaly, there are no specific “causes” in the way that acquired conditions have causes. It is a normal variation in the anatomy that some individuals are born with.
What is the treatment for a septate hymen?
The treatment for a septate hymen generally involves a minor surgical procedure called a hymenectomy. This surgery is simple and can effectively resolve any symptoms or issues related to the condition. During a hymenectomy, the extra band of tissue in the hymen is carefully cut and removed, allowing for the creation of a single, normal-sized vaginal opening. This procedure is usually performed on an outpatient basis, meaning the patient can return home the same day. It can be done under local anesthesia, general anesthesia, or sedation, depending on the patient’s needs and the healthcare provider’s recommendation.
After the procedure, some mild discomfort or spotting may occur, but these symptoms typically subside quickly. Patients are usually advised to avoid inserting anything into the vagina, such as tampons, and to refrain from sexual activity for a few weeks to ensure proper healing. Follow-up appointments may be scheduled to monitor healing and ensure there are no complications.
Treatment is generally recommended if the septate hymen is causing significant symptoms, such as pain during tampon use, difficulty with sexual intercourse, or problems with menstrual flow. However, if the septate hymen is discovered incidentally and is not causing any issues, treatment may not be necessary. A hymenectomy is a safe and effective procedure with a high success rate, usually resolving any symptoms related to a septate hymen.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.