What are the symptoms of scalp psoriasis?
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects the scalp, often leading to various symptoms, including:
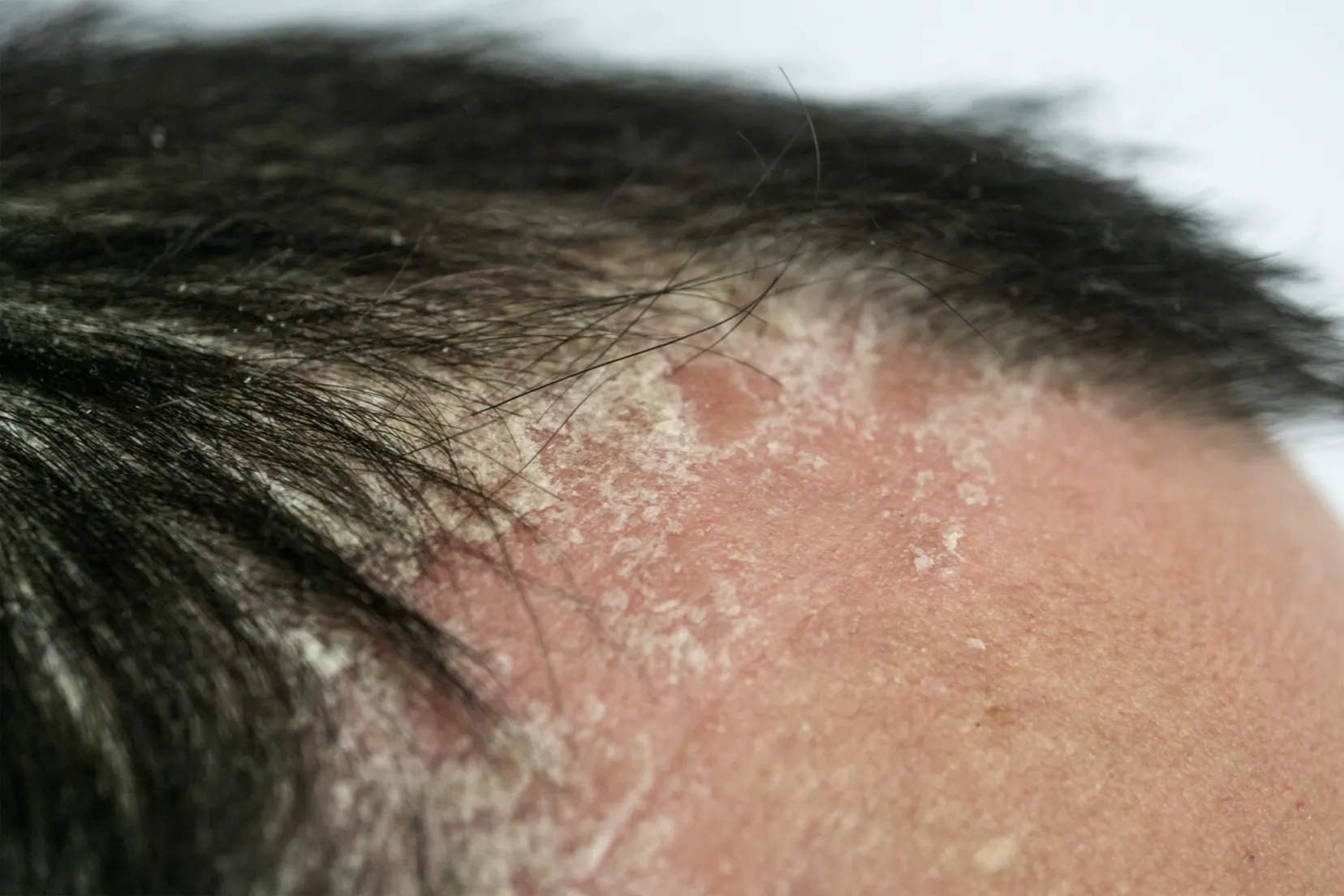
- Red Patches: Raised, red patches of skin covered with silvery-white scales. These patches can be dry and flaky.
- Itching: Persistent itching of the scalp, which can range from mild to severe.
- Dryness: The scalp may feel dry and tight, with a dry, flaky appearance.
- Flaking: Scales or flakes that can be visible on the scalp and may fall onto clothing or shoulders, often mistaken for dandruff.
- Burning Sensation: Some people experience a burning or soreness in the affected areas.
- Hair Loss: In severe cases, scratching or the buildup of scales can lead to temporary hair loss in the affected areas.
- Cracked Skin: The skin on the scalp can become cracked or fissured, particularly in severe cases.
- Discomfort: The affected areas may feel uncomfortable or tender.
Scalp psoriasis can vary in severity from mild flaking to extensive, inflamed patches. If you experience symptoms that do not improve with over-the-counter treatments, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider or dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
What are the causes of scalp psoriasis?
Scalp psoriasis is a complex condition with several contributing factors:
- Genetics: A family history of psoriasis or other autoimmune conditions can increase the risk of developing scalp psoriasis. It is thought to have a genetic component that predisposes individuals to the condition.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Scalp psoriasis is considered an autoimmune disorder. In this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to rapid skin cell turnover and the formation of psoriasis plaques.
- Environmental Triggers: Various environmental factors can trigger or exacerbate scalp psoriasis, including:
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress can trigger flare-ups.
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections, such as streptococcal throat infections, can trigger or worsen symptoms.
- Injury to the Skin: Physical trauma to the skin, such as cuts, scratches, or sunburn, can trigger a psoriasis flare-up, a phenomenon known as the Koebner response.
- Climate: Extreme weather conditions, especially cold and dry weather, can exacerbate symptoms.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can influence the onset or severity of scalp psoriasis.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as lithium, beta-blockers, and antimalarials, can trigger or worsen psoriasis.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking and heavy alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing psoriasis or exacerbate existing symptoms.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing psoriasis and can make the condition more severe.
While these factors can contribute to the development or worsening of scalp psoriasis, the exact cause is not fully understood and likely involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. If you have symptoms of scalp psoriasis, consulting with a healthcare provider or dermatologist is recommended for diagnosis and management.
What is the treatment for scalp psoriasis?
Treating scalp psoriasis often involves a combination of topical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes systemic medications. Here’s a comprehensive approach:
- Topical Treatments:
- Medicated Shampoos: Shampoos containing coal tar or salicylic acid can help reduce scaling and inflammation.
- Topical Steroids: Corticosteroid creams or solutions can reduce inflammation and itching.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: Medications like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus can be used for their anti-inflammatory effects.
- Topical Vitamin D Analogues: Products containing calcipotriene can help slow down skin cell growth.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision can help reduce symptoms. This treatment may involve narrow-band UVB light or PUVA (psoralen plus UVA) therapy.
- Systemic Medications: For severe cases, oral or injected medications may be necessary:
- Oral Medications: Drugs such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or acitretin can help manage symptoms by affecting the immune system or skin cell turnover.
- Biologics: These are newer, targeted treatments that are administered by injection or infusion and work by targeting specific immune system proteins involved in psoriasis.
- Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the scalp moisturized with emollients can help reduce dryness and flaking.
- Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding personal triggers, such as stress, certain medications, or skin injuries, can help manage flare-ups.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet may help improve overall skin health and reduce inflammation.
- Home Care:
- Scalp Massage: Gently massaging the scalp with natural oils like coconut oil can help loosen scales and soothe irritation.
- Gentle Hair Care: Use mild, non-irritating shampoos and avoid excessive heat or harsh hair treatments.
- Consult a Dermatologist: Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider or dermatologist is important for monitoring the condition and adjusting treatments as needed.
Scalp psoriasis treatment is often personalized, so working with a healthcare provider to develop an effective treatment plan tailored to your specific needs is crucial.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.