What are the symptoms of scalp pimples and acne?
Scalp pimples and acne can cause a range of symptoms, including:
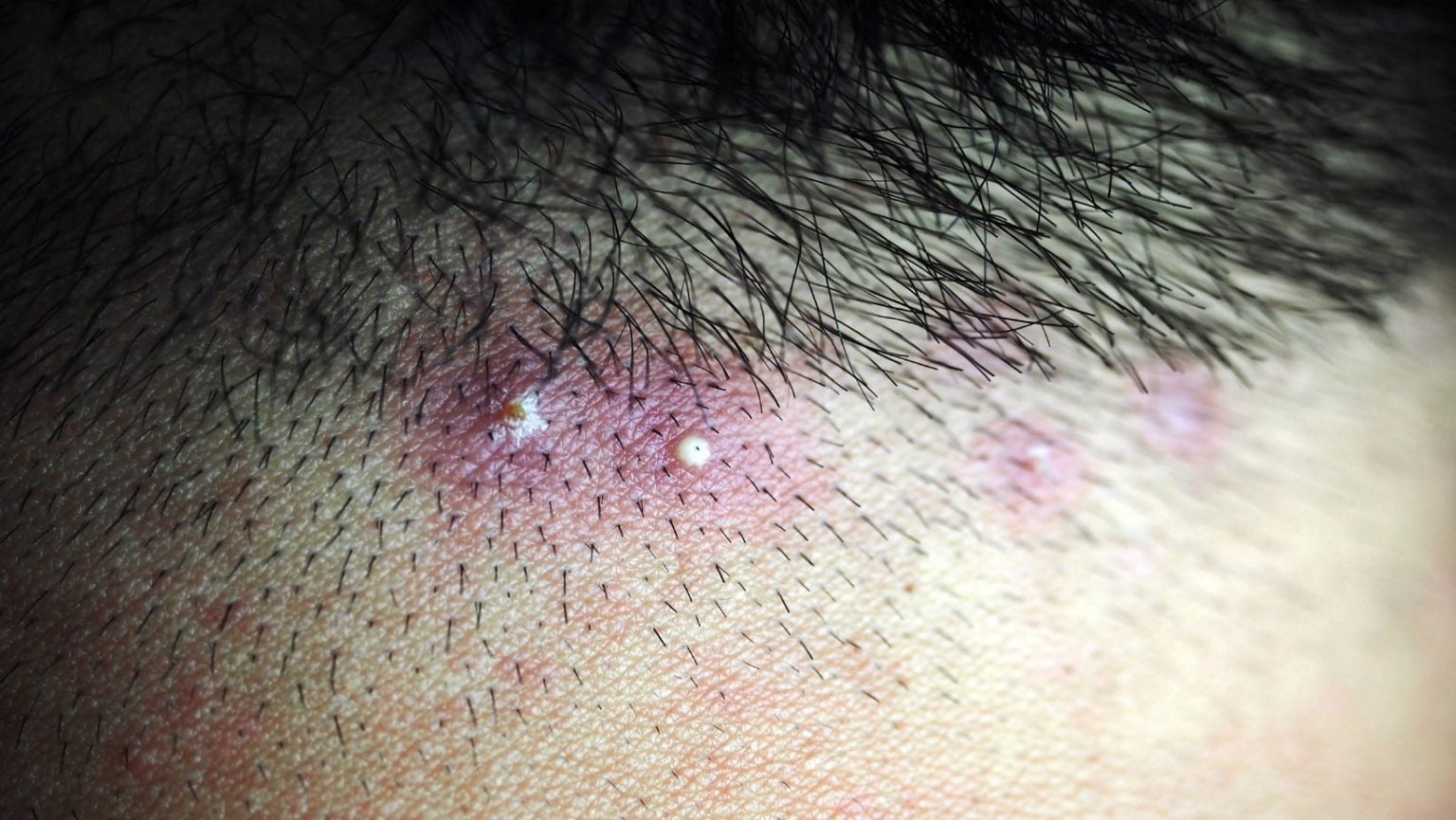
- Red Bumps: Small, red, and inflamed bumps on the scalp, which may be tender to the touch.
- Whiteheads and Blackheads: Similar to facial acne, these can appear on the scalp as white or black dots.
- Itching: Itchy scalp or the area around the pimples, which can lead to scratching and potential irritation.
- Pain: Tenderness or discomfort in the affected areas, especially if the pimples are large or inflamed.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the pimples can cause localized swelling on the scalp.
- Scabs: If pimples are scratched or picked, they can become crusty or form scabs.
- Hair Loss: In severe cases, inflammation and irritation may lead to temporary hair thinning or loss in the affected areas.
- Oily or Dry Scalp: The scalp may appear excessively oily or dry, depending on the underlying cause of the acne.
These symptoms can be associated with various conditions, including scalp acne, folliculitis (inflammation of hair follicles), or seborrheic dermatitis. If you have persistent or severe symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What are the causes of scalp pimples and acne?
Scalp pimples and acne can be caused by several factors:
- Excess Oil Production: Overactive sebaceous (oil) glands can lead to an excess of oil on the scalp, which can clog hair follicles and contribute to acne.
- Hair Products: Use of certain hair products like shampoos, conditioners, and styling products can cause buildup on the scalp, leading to clogged pores and pimples. Products containing oils, silicones, or heavy fragrances are often culprits.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as those experienced during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or due to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can increase oil production and contribute to scalp acne.
- Poor Hygiene: Infrequent washing of the hair and scalp can lead to a buildup of oil, sweat, and dead skin cells, increasing the risk of acne.
- Bacterial or Fungal Infections: Infections such as folliculitis (inflammation of hair follicles) can cause pimples on the scalp. Fungal infections, such as those caused by Malassezia yeast, can also contribute to scalp issues.
- Diet: Although the relationship between diet and acne is still debated, some studies suggest that high-glycemic diets or diets high in dairy products may exacerbate acne.
- Stress: Stress can impact hormone levels and oil production, potentially leading to acne flare-ups.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, sweat, and other environmental factors can irritate the scalp and contribute to acne.
- Tight Headwear: Wearing tight hats, helmets, or headbands can trap sweat and oil, leading to clogged pores and pimples.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis or psoriasis can cause scalp inflammation and contribute to acne-like symptoms.
Addressing these causes through proper scalp hygiene, using non-comedogenic hair products, managing stress, and maintaining a balanced diet can help prevent and manage scalp pimples and acne. If the condition persists or worsens, consulting a healthcare provider or dermatologist is recommended.
What is the treatment for scalp pimples and acne?
Treating scalp pimples and acne involves a combination of good hygiene practices, topical treatments, and lifestyle adjustments. Here’s a comprehensive approach:
- Medicated Shampoos: Use shampoos containing ingredients like salicylic acid, ketoconazole, or zinc pyrithione to help reduce inflammation, control oil production, and treat fungal or bacterial infections.
- Topical Treatments: Apply topical treatments specifically designed for acne, such as benzoyl peroxide or retinoids, to affected areas of the scalp. These can help unclog pores and reduce inflammation.
- Avoid Irritants: Choose hair products that are non-comedogenic and free from heavy oils, silicones, and harsh chemicals. Opt for products labeled as “gentle” or “for sensitive skin.”
- Regular Washing: Maintain a regular hair-washing routine to keep the scalp clean and remove excess oil, sweat, and buildup. Use a mild, sulfate-free shampoo to avoid irritation.
- Avoid Tight Headwear: Reduce the use of tight hats, helmets, or headbands that can trap sweat and oil on the scalp.
- Balanced Diet: Consider adjusting your diet to include fewer high-glycemic foods and dairy products, which may exacerbate acne. Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as exercise, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to help manage stress levels, which can impact acne.
- Consult a Dermatologist: For persistent or severe cases, seek advice from a dermatologist. They may prescribe stronger topical or oral medications, such as antibiotics, hormonal treatments, or retinoids.
- Proper Hair Care: Avoid excessive scratching or picking at the scalp, as this can lead to irritation and secondary infections. Gently massage the scalp when washing to avoid unnecessary trauma.
- Hydration: Ensure adequate hydration to support overall skin health.
Treating scalp acne effectively involves addressing both the symptoms and underlying causes. If over-the-counter treatments are not effective, professional medical advice and treatment may be necessary.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.