What are the symptoms of tooth discoloration?
Tooth discoloration can present in various ways, depending on its cause and severity. Symptoms include:
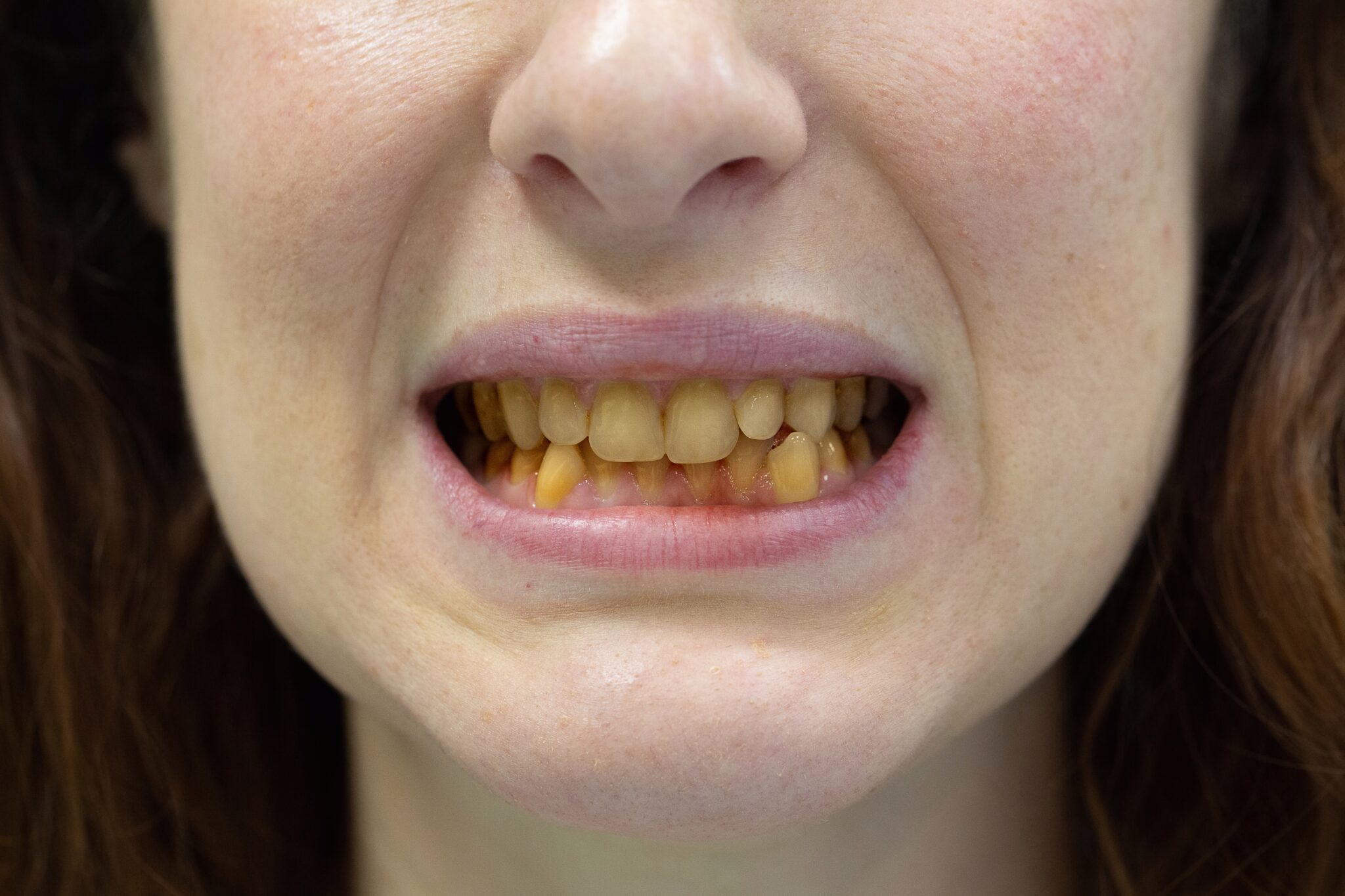
- Color Changes: Teeth may appear yellow, brown, gray, or have a general dullness compared to their natural shade.
- Spots or Stains: You may notice specific spots or patches of different colors on the teeth. These can be white, yellow, or brown.
- Uneven Color: The discoloration might be uneven, with some teeth appearing more discolored than others.
- Changes in Brightness: The overall brightness of the teeth may decrease, making them look less vibrant or shiny.
- Surface Texture Changes: In some cases, the affected areas might also feel rough or different in texture compared to the rest of the tooth.
The underlying causes of tooth discoloration can include factors like dietary habits, smoking, poor oral hygiene, aging, medications, and certain medical conditions. Identifying the specific cause can help determine the appropriate treatment to address the discoloration.
What are the causes of tooth discoloration?
Tooth discoloration can arise from a variety of causes, including:
- Dietary Habits: Consuming foods and drinks that stain teeth, such as coffee, tea, red wine, and certain berries.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Nicotine and tar from tobacco products can lead to yellow or brown stains on teeth.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, which can contribute to discoloration.
- Aging: As people age, the enamel on their teeth can wear down, making the underlying dentin more visible, which can lead to a yellowed appearance.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as tetracycline antibiotics and some antihistamines, can cause staining. Also, high doses of fluoride during childhood can cause fluorosis, leading to white or brown spots.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as jaundice or certain metabolic disorders can affect tooth color.
- Genetics: Some people may have naturally darker or lighter teeth due to genetic factors.
- Trauma: Injury to a tooth can lead to internal discoloration, often resulting in a gray or darkened appearance.
- Excessive Fluoride: Overexposure to fluoride during tooth development (for example, from fluoride supplements or high-fluoride water) can cause dental fluorosis, resulting in white spots or streaks on the teeth.
Understanding the cause of tooth discoloration is crucial for choosing the most effective treatment to restore the natural appearance of your teeth.
What is the treatment for tooth discoloration?
The treatment for tooth discoloration depends on the cause and extent of the staining. Common treatments include:
- Professional Whitening: Dentists offer whitening treatments that use stronger agents than over-the-counter products. These treatments can be more effective for significant or deep stains.
- Over-the-Counter Whitening Products: These include whitening toothpaste, strips, and gels. They are generally effective for surface stains but may not work as well for deeper discoloration.
- Veneers: Dental veneers are thin shells of porcelain or composite resin that cover the front surface of the teeth. They can mask discoloration and improve the appearance of teeth with severe staining.
- Bonding: Dental bonding involves applying a tooth-colored resin to the affected teeth. This can cover stains and improve the appearance of teeth.
- Crowns: For severely discolored or damaged teeth, crowns (caps) can cover and protect the tooth while improving its appearance.
- Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste, flossing, and routine dental cleanings can help prevent and reduce surface stains.
- Avoiding Stain-Causing Foods and Drinks: Reducing consumption of coffee, tea, red wine, and other staining substances can help prevent further discoloration.
- Quit Smoking: Stopping tobacco use can prevent additional staining and improve overall dental health.
- Fluoride Treatment: For those with fluoride-related discoloration, fluoride treatments or reduced fluoride exposure may help.
Consulting a dentist is advisable to determine the most appropriate treatment based on the specific cause and severity of the tooth discoloration.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.