What are the symptoms of tinea manuum?
Tinea manuum is a fungal infection that affects the hands, and its symptoms can include:
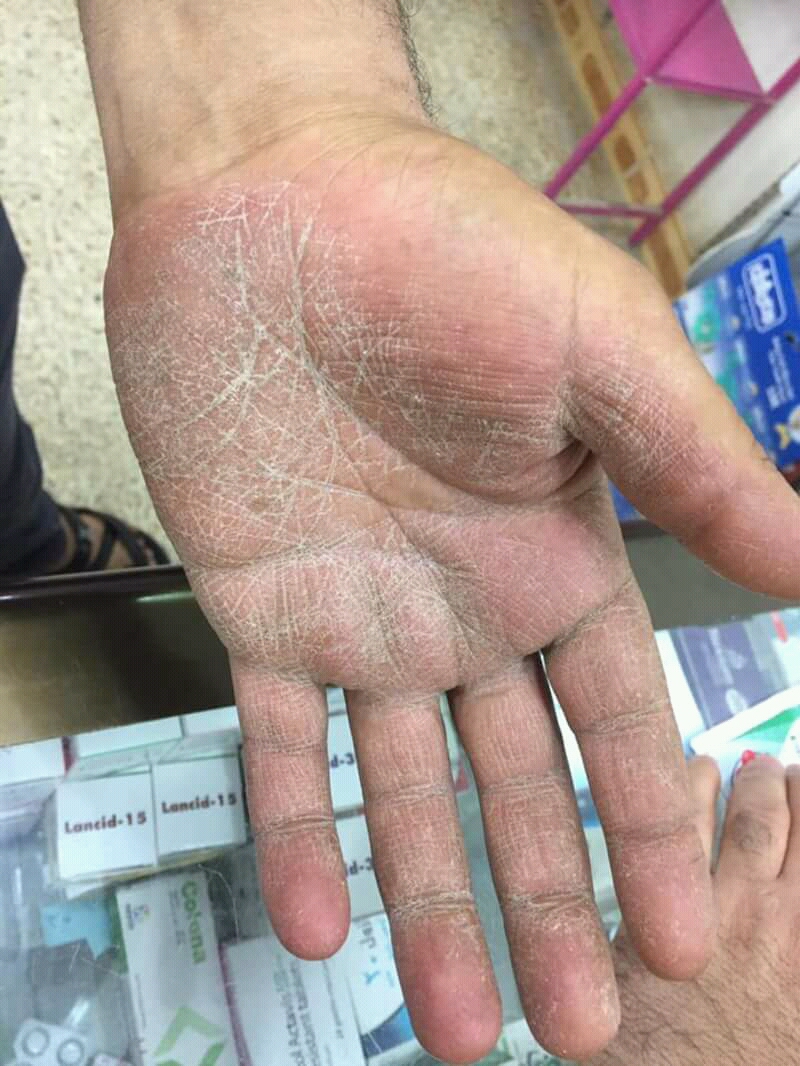
- Red, Itchy Rash: The skin on the hands may develop a red, itchy rash. The rash can sometimes appear as a ring-like pattern or patch.
- Scaling and Peeling: The affected areas often show scaling or peeling of the skin, which may be more pronounced around the edges of the rash.
- Dry, Cracked Skin: The skin may become dry and cracked, particularly in severe cases.
- Blisters or Vesicles: Small blisters or vesicles may develop, which can become crusty or scaly as they heal.
- Discoloration: The affected skin can become discolored, appearing lighter or darker than the surrounding skin.
Tinea manuum is caused by dermatophyte fungi and can spread through direct contact with infected individuals, contaminated objects, or surfaces.
What are the causes of tinea manuum?
Tinea manuum is caused by dermatophyte fungi, which are responsible for fungal infections of the skin. The main causes and contributing factors include:
- Direct Contact: Direct contact with an infected person or their skin can spread the fungi. This includes touching the infected area or coming into contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Contaminated Objects: Sharing or using contaminated items such as towels, gloves, or sports equipment can facilitate the spread of the infection.
- Exposure to Infected Animals: Contact with animals that are carriers of dermatophyte fungi, such as pets with ringworm, can lead to infection.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate hand hygiene and not washing hands regularly can contribute to the spread and development of tinea manuum.
- Warm, Moist Environments: Fungi thrive in warm, moist conditions. Environments that promote sweating or humidity can increase the risk of fungal infections.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems such as HIV/AIDS or underlying health conditions may be more susceptible to fungal infections.
Taking preventive measures such as maintaining good hand hygiene, avoiding sharing personal items, and treating any fungal infections promptly can help reduce the risk of tinea manuum.
What is the treatment for tinea manuum?
The treatment for tinea manuum typically involves antifungal medications and proper hygiene practices. Here’s a general approach:
- Oral Antifungal Medications: Prescription oral antifungal drugs, such as terbinafine, itraconazole, or griseofulvin, are commonly used to treat tinea manuum. These medications are effective in eliminating the fungal infection from the skin.
- Topical Antifungal Treatments: In some cases, topical antifungal creams, lotions, or ointments containing clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine may be recommended. These are applied directly to the affected areas of the hand.
- Good Hand Hygiene: Regularly washing hands with antifungal soap and ensuring the hands are kept clean and dry can help prevent the spread of the infection and aid in healing.
- Avoiding Contamination: It is important to avoid sharing personal items, such as towels and gloves, and to disinfect or avoid using contaminated objects or surfaces.
- Treatment of Secondary Infections: If secondary bacterial infections develop, additional treatment with antibiotics may be necessary.
- Regular Follow-Up: Follow-up with a healthcare provider may be needed to monitor the progress of treatment and ensure the infection is resolved.
Adhering to the prescribed treatment regimen and practicing good hygiene are crucial for effectively managing tinea manuum and preventing recurrence or transmission.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.