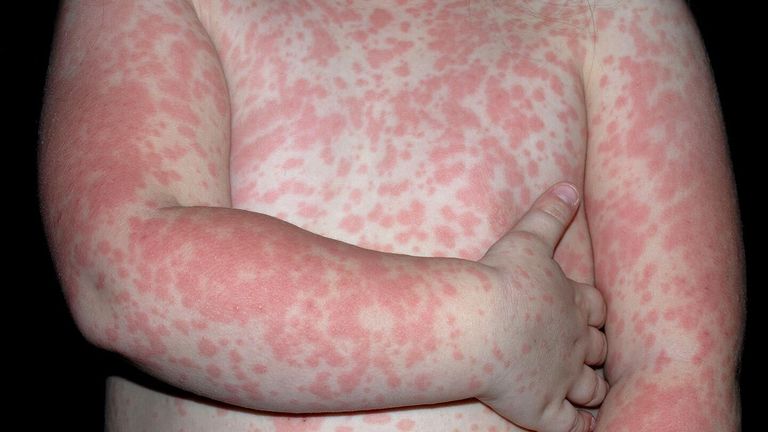
What are the symptoms of a skin rash?
The symptoms of a skin rash can vary widely depending on the underlying cause and type of rash, but common symptoms include:
- Redness: The skin may appear red or inflamed.
- Itching: Itchiness is often a prominent symptom, ranging from mild to severe.
- Swelling: The affected area may become swollen or puffy.
- Bumps or Hives: Rashes may present as raised bumps or hives.
- Blisters: Small fluid-filled blisters can develop, especially in conditions like chickenpox or herpes.
- Dry, Scaly Skin: Some rashes, like those associated with eczema or psoriasis, may cause dry, flaky patches.
- Crusting or Oozing: The rash may become crusty or ooze fluid, especially if scratched or infected.
- Pain: In some cases, a rash can be painful or tender to the touch.
- Changes in Skin Color: The skin may darken or lighten in the affected area, especially with chronic conditions.
- Flaking or Peeling: The skin may flake off or peel away, as seen in conditions like psoriasis.
The appearance and location of the rash, along with associated symptoms such as fever or general discomfort, can help in diagnosing the underlying cause. If you have a rash with persistent or severe symptoms, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What are the causes of a skin rash?
A skin rash can result from a variety of causes, including:
- Allergic Reactions: Contact with allergens such as certain foods, medications, or materials (e.g., latex, nickel) can trigger rashes.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause rashes. Examples include impetigo, chickenpox, shingles, and ringworm.
- Skin Conditions: Chronic skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis can lead to persistent rashes.
- Heat: Heat rash, or prickly heat, occurs when sweat is trapped in the skin’s pores, leading to red, itchy bumps.
- Insect Bites: Bites from insects such as mosquitoes, fleas, or bedbugs can cause localized rashes.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus or vasculitis can cause rashes as part of the immune system’s response.
- Drug Reactions: Certain medications can cause allergic reactions or side effects that manifest as rashes.
- Environmental Irritants: Exposure to irritants like harsh chemicals, soaps, or detergents can result in contact dermatitis.
- Stress: High levels of stress can exacerbate or trigger skin conditions leading to rashes.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Systemic illnesses such as liver disease or kidney failure can sometimes cause skin rashes as part of a broader symptom complex.
Identifying the cause of a rash often involves considering the rash’s appearance, location, and associated symptoms, along with any recent exposures or changes in health.
What is the treatment for a skin rash?
The treatment for a skin rash depends on its underlying cause, but general approaches include:
- Avoiding Irritants: Identifying and avoiding triggers or allergens that caused the rash can help prevent it from worsening. For example, changing soaps or detergents if they are identified as irritants.
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter creams or ointments, such as hydrocortisone cream, calamine lotion, or antifungal creams, can alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation or itching.
- Moisturizers: Applying emollients or moisturizers can help soothe dry or irritated skin, especially in conditions like eczema.
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines can help relieve itching and allergic reactions if the rash is due to an allergy.
- Medications: Prescription medications, such as stronger corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, may be needed for more severe or chronic rashes like psoriasis or dermatitis.
- Antibiotics: If the rash is due to a bacterial infection, topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed.
- Antifungals: For fungal infections, antifungal creams or oral medications may be required.
- Cool Compresses: Applying cool, damp cloths to the affected area can help reduce itching and inflammation.
- Avoiding Scratching: Keeping the rash clean and avoiding scratching can prevent further irritation or infection.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: For heat rash, staying cool and dry can help prevent recurrence.
For persistent, severe, or unexplained rashes, it’s important to seek medical advice for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.