What are the symptoms of a segmental fracture?
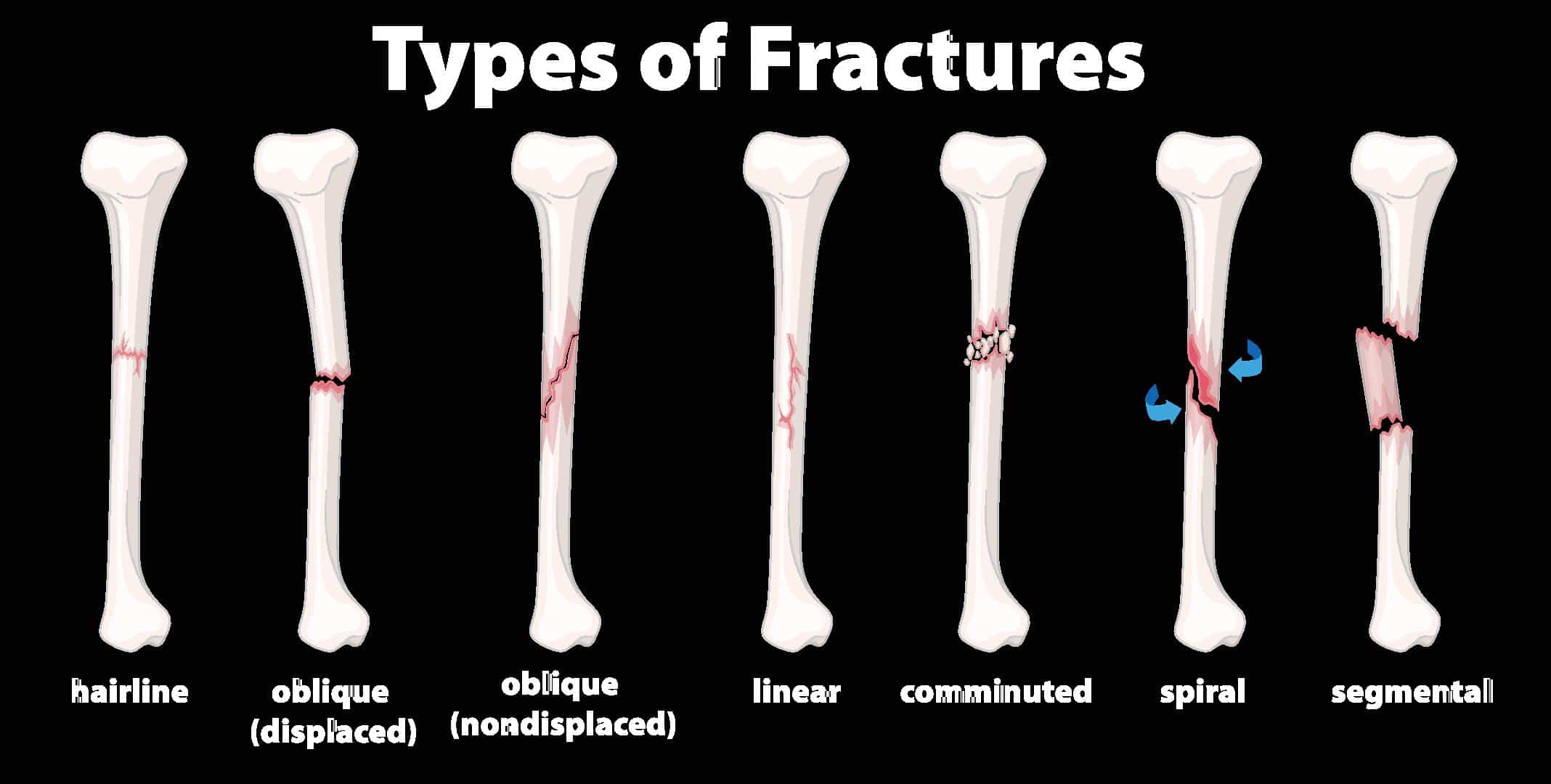
A segmental fracture, also known as a segmental bone fracture, involves the breaking of a bone into two or more separate segments, often resulting in a “broken” or “shattered” appearance. The symptoms of a segmental fracture typically include:
- Severe Pain: Intense pain at the site of the fracture, which may worsen with movement or pressure.
- Swelling: Significant swelling around the fracture site, due to inflammation and accumulation of fluid.
- Bruising: Discoloration or bruising around the area of the fracture.
- Deformity: Visible deformity or abnormal positioning of the bone, where the segments may be out of alignment.
- Difficulty Moving: Limited or impaired ability to move the affected limb or joint, depending on the location of the fracture.
- Tenderness: The area around the fracture is often tender to the touch.
- Functional Loss: Reduced function of the affected limb or body part, which may affect daily activities.
- Bone Fragments: In some cases, fragments of bone may be visible or palpable if the fracture is open or there is a risk of the bone piercing through the skin.
A segmental fracture often requires immediate medical attention to properly realign and stabilize the bone segments, as well as to prevent complications such as infection, improper healing, or loss of function.
What are the causes of a segmental fracture?
A segmental fracture occurs when a bone breaks into two or more segments, usually due to significant trauma or stress. The common causes of segmental fractures include:
- High-Energy Trauma: Severe impacts, such as those experienced in car accidents, falls from heights, or violent collisions, can cause segmental fractures due to the intense force exerted on the bone.
- Sports Injuries: Contact sports or activities involving sudden, high-impact forces, like football, soccer, or skiing, can lead to segmental fractures, especially when the bone is subjected to extreme stress or direct blows.
- Crushing Injuries: Situations where the body or limb is crushed or pinched between heavy objects can result in segmental fractures.
- Repeated Stress: Overuse or repetitive stress on a bone, particularly in high-intensity activities, can lead to stress fractures that may eventually progress to segmental fractures if not managed properly.
- Bone Weakness: Conditions that weaken bones, such as osteoporosis or bone cancer, can make them more susceptible to fractures. In these cases, even minor trauma may lead to segmental fractures.
- Falls: Falling from a significant height or onto a hard surface can cause segmental fractures due to the force of the impact.
Segmental fractures require careful evaluation and treatment to ensure proper healing and to prevent complications.
What is the treatment for a segmental fracture?
Treating a segmental fracture involves several steps to ensure proper healing and restore function. Initially, immediate care focuses on immobilizing the affected area to prevent further damage and managing pain with medications and ice application to reduce swelling.
A thorough medical evaluation is necessary, including imaging studies like X-rays to assess the fracture’s severity and alignment. Depending on the fracture’s characteristics, treatment may involve realigning the bone segments. This can be done non-surgically, known as closed reduction, or through surgical means, called open reduction.
Surgical intervention might involve internal fixation using plates, screws, or rods to stabilize the bone internally, or external fixation where an external frame supports the bone from outside.
Rehabilitation is crucial for recovery and typically includes physical therapy to restore strength, flexibility, and function. Exercises are prescribed to improve mobility and prevent stiffness or muscle atrophy.
Ongoing care includes regular follow-up appointments to monitor healing and address any complications, such as infection or improper bone healing. If surgery was performed, proper wound care is essential to prevent infection and ensure healing. Managing any complications that arise, such as delayed or improper healing, is also important to achieving a successful recovery.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.