What are the symptoms of sarcopenia?
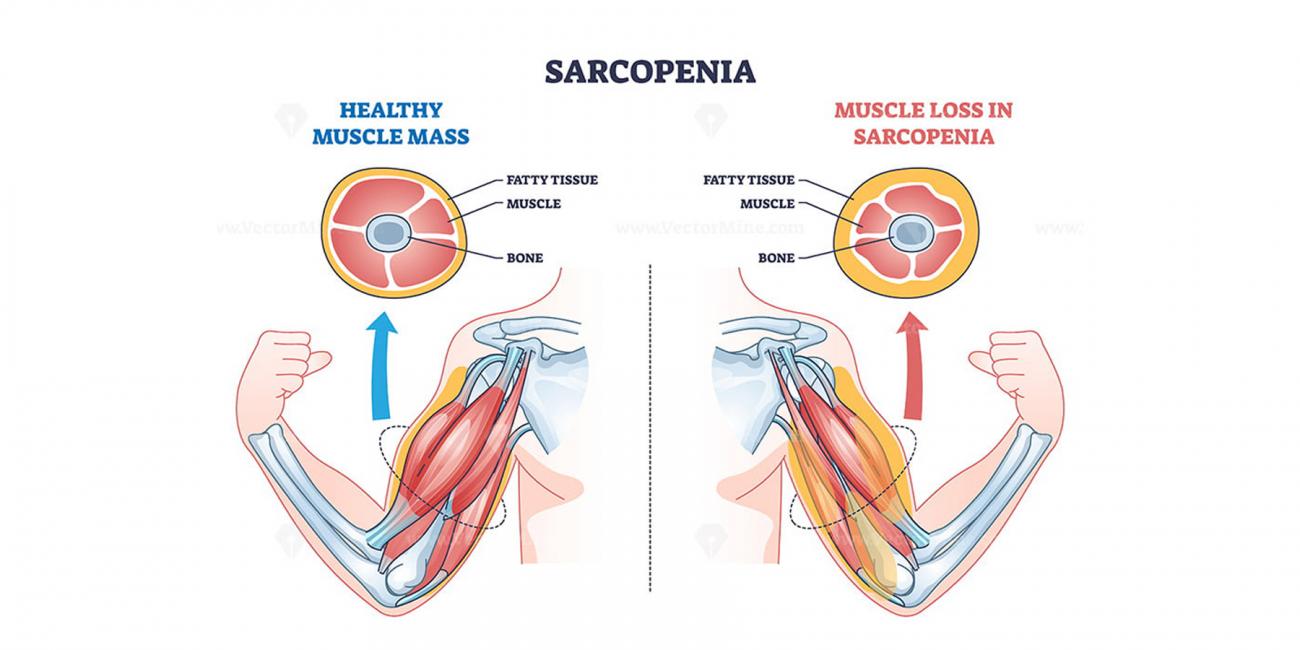
Sarcopenia is the loss of muscle mass and strength associated with aging, which can impact physical function and overall health. Common symptoms include:
- Muscle Weakness: Reduced strength in the arms, legs, or other muscles, making it harder to perform everyday tasks like lifting objects or climbing stairs.
- Decreased Muscle Mass: Noticeable loss of muscle size, leading to a decrease in muscle bulk and definition.
- Fatigue: Increased feelings of tiredness and reduced stamina during physical activities.
- Impaired Mobility: Difficulty walking, frequent falls, or unsteadiness while moving due to weakened muscles.
- Reduced Physical Performance: Difficulty with activities that require strength or endurance, such as carrying groceries or engaging in recreational activities.
- Weight Loss: Loss of muscle mass can lead to unintended weight loss or a decrease in body weight.
- Poor Posture: Changes in posture, such as a hunched back, due to weakened core and back muscles.
- Slow Gait: A noticeable decrease in walking speed, which can be a sign of reduced muscle function and strength.
- Difficulty in Performing Daily Activities: Struggles with routine tasks like getting out of a chair, dressing, or bathing independently.
These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and independence. Early recognition and intervention, including strength training exercises, proper nutrition, and lifestyle modifications, are important for managing and potentially mitigating the effects of sarcopenia.
What are the causes of sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia, the age-related loss of muscle mass and strength, is caused by a combination of factors:
- Aging: The primary cause of sarcopenia is aging, which leads to a natural decline in muscle mass and function over time. This process is influenced by changes in muscle protein synthesis and breakdown.
- Hormonal Changes: Decreases in hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, and growth hormone with age can contribute to muscle loss and reduced muscle strength.
- Inactivity: Sedentary lifestyle and physical inactivity can accelerate muscle loss. Regular physical activity, particularly strength training, is crucial for maintaining muscle mass and function.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of protein and essential nutrients can impair muscle protein synthesis and contribute to muscle loss. Malnutrition or poor dietary habits can exacerbate sarcopenia.
- Chronic Diseases: Conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can contribute to muscle loss and weakness.
- Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation, often associated with aging or certain diseases, can promote muscle breakdown and impair muscle regeneration.
- Genetics: Genetic factors can influence an individual’s susceptibility to sarcopenia and the rate of muscle loss.
- Neurological Factors: Changes in the nervous system, including decreased motor neuron function, can affect muscle activation and contribute to muscle weakness.
- Muscle Protein Turnover: Imbalance between muscle protein synthesis and breakdown can lead to net muscle loss. Aging can disrupt this balance, leading to increased muscle degradation.
- Pain and Disability: Conditions causing pain or disability, such as arthritis, can reduce physical activity and contribute to muscle loss.
- Medication Side Effects: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can contribute to muscle loss and weakness.
Addressing these factors through a combination of exercise, nutrition, and medical management can help mitigate the effects of sarcopenia and improve muscle health and function.
What is the treatment for sarcopenia?
Treating sarcopenia involves a multifaceted approach focusing on improving muscle mass, strength, and function. Key strategies include:
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, especially resistance or strength training exercises, is crucial. These exercises help build and maintain muscle mass and strength. Aerobic exercises can also improve overall physical function and endurance.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in protein and essential nutrients is important for muscle health. Ensuring adequate protein intake (e.g., lean meats, dairy products, legumes) and incorporating foods high in vitamins and minerals, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can support muscle protein synthesis.
- Supplementation: In some cases, dietary supplements such as protein powders, vitamin D, and branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) may be recommended to address deficiencies and support muscle health.
- Medical Management: Managing chronic diseases and conditions that contribute to sarcopenia is essential. This may involve medications or therapies to address underlying health issues that impact muscle health.
- Physical Therapy: Working with a physical therapist can help develop a personalized exercise program, improve mobility, and address specific functional limitations related to sarcopenia.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, a nutritious diet, adequate hydration, and sufficient sleep can help mitigate the effects of sarcopenia.
- Fall Prevention: For individuals at risk of falls due to muscle weakness, implementing fall prevention strategies, such as home safety modifications and balance training, is important to reduce the risk of injury.
- Hormone Therapy: In some cases, hormone replacement therapy may be considered, especially if hormonal imbalances are contributing to muscle loss. This should be evaluated and managed by a healthcare provider.
- Regular Monitoring: Ongoing assessment of muscle mass, strength, and physical function can help track progress and adjust treatment strategies as needed.
Addressing sarcopenia early and comprehensively can help improve muscle health, physical function, and overall quality of life.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.