What are the symptoms of psoriasis on the hands and feet?
Psoriasis on the hands and feet can manifest with a range of symptoms:
- Red, Inflamed Skin: Psoriasis commonly presents as red patches of inflamed skin that may be covered with silvery scales.
- Dry, Cracked Skin: The skin on the hands and feet can become dry and may develop cracks or fissures, which can be painful and prone to bleeding.
- Thickened Skin: The affected areas may show thickened, hardened skin, often referred to as palmoplantar psoriasis when it occurs on the palms and soles.
- Nail Changes: Psoriasis can cause changes in the nails, including pitting (small depressions), discoloration, thickening, and separation from the nail bed.
- Itching and Burning: The affected areas often itch and may cause a burning sensation.
- Pain: Psoriasis on the hands and feet can lead to significant discomfort and pain, particularly with movement or pressure.
- Swelling and Stiffness: In some cases, psoriatic arthritis may accompany hand and foot psoriasis, leading to swelling, stiffness, and joint pain.
These symptoms can impact daily activities and quality of life, making effective management important.
What are the causes of psoriasis on the hands and feet?
Psoriasis on the hands and feet is influenced by several factors:
- Genetic Factors: Psoriasis has a strong genetic component. If you have a family history of psoriasis, you may be more susceptible to developing it on your hands and feet.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to rapid skin cell turnover and the formation of plaques.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical trauma or injury to the hands or feet, such as cuts, scrapes, or burns, can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis. This is known as the Koebner phenomenon.
- Infections: Certain infections, particularly streptococcal infections (strep throat), can trigger or worsen psoriasis outbreaks.
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress can trigger flare-ups or make existing psoriasis symptoms worse.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environmental triggers, such as cold weather, dry air, or irritants, can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms.
- Certain Medications: Some medications can trigger or worsen psoriasis, including lithium, beta-blockers, and antimalarials.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to the development or worsening of psoriasis.
- Other Medical Conditions: Conditions like metabolic syndrome and obesity may also influence the severity and location of psoriasis.
What is the treatment for psoriasis on the hands and feet?
Treating psoriasis on the hands and feet involves a combination of topical treatments, systemic medications, and lifestyle modifications:
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroid creams are commonly used to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. Other topical options include vitamin D analogs, tar products, and topical calcineurin inhibitors.
- Moisturizers: Regular use of thick, emollient moisturizers can help keep the skin hydrated and reduce dryness and cracking.
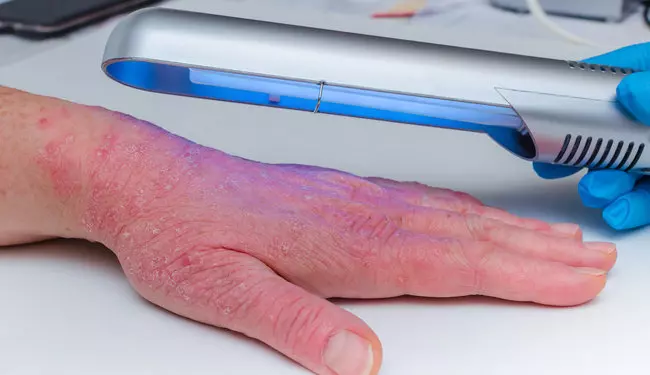
- Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision can help reduce psoriasis symptoms. This can be especially effective for psoriasis on the hands and feet.
- Systemic Medications: For more severe cases, oral or injected medications that affect the entire body, such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or biologics, may be prescribed.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, avoiding triggers (like quitting smoking and excessive alcohol), and protecting the skin from injury can help manage symptoms.
- Occupational Therapy: For psoriasis affecting the hands, therapy may help with daily activities and reduce the impact of symptoms on hand function.
- Foot Care: For psoriasis on the feet, regular foot care and wearing comfortable, non-irritating footwear can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Avoiding Irritants: Minimize exposure to harsh chemicals or irritants that can worsen symptoms.
Always consult a healthcare provider for a treatment plan tailored to individual needs and to monitor for potential side effects or interactions.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.